
Thus the 5W-30 oils were introduced, rather than the fixed and temperature limiting grades – where the thin oils became too thin when hot and the thicker oils became too thick when cold. Thus the issue of multigrade oils came into being, where with variable temperatures of, say, −10 ☌ during the cold nights and 20 ☌ during the days, a 5 weight oil would be good as the oil would be pumpable in a cold engine and as the engine came up to running temperature, and the day warmed up, the characteristics of a 30 weight oil would be ideal. However, in hot climates, where temperatures range from 30 ☌ to 45 ☌, a 50 weight oil would be necessary, so it would remain thick enough to hold up an oil film between the moving hot parts. As an example, with winter oils and cold starting the engines, and with temperature ranges from, say, −30 ☌ to 0 ☌, a 5 weight oil would be pumpable at the very low temperatures and the generally cooler engine operating temperatures. Historically, there were two different oil types recommended for usage in different weather conditions. This provides consistent engine performance within the normal working conditions. The best oils with the highest VI will remain stable and not vary much in viscosity over the temperature range. Many lubricant applications require the lubricant to perform across a wide range of conditions, for example, automotive lubricants are required to reduce friction between engine components when the engine is started from cold (relative to the engine's operating temperatures) up to 200 ☌ (392 ☏) when it is running. If the lubricant is too viscous, it will require a large amount of energy to move (as in honey) if it is too thin, the surfaces will come in contact and friction will increase. Generally, the least viscous lubricant which still forces the two moving surfaces apart to achieve " fluid bearing" conditions is desired. The viscosity of a lubricant is closely related to its ability to reduce friction in solid body contacts.
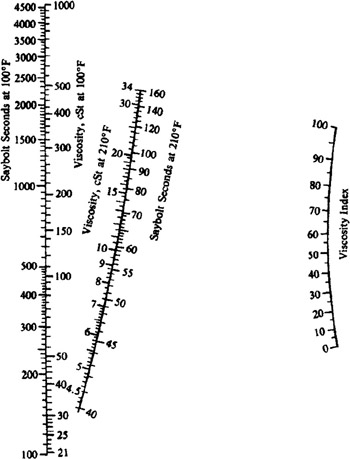
The VI was originally measured on a scale from 0 to 100 however, advancements in lubrication science have led to the development of oils with much higher VIs. The higher the VI, the more stable the viscosity remains over some temperature range. The lower the VI, the more the viscosity is affected by changes in temperature. It is mostly used to characterize the viscosity-temperature behavior of lubricating oils. The viscosity index ( VI) is an arbitrary, unit-less measure of a fluid's change in viscosity relative to temperature change.


Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. This article needs additional citations for verification.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
